Industrial Spare Parts — Engineered for Maximum Uptime
Precision-engineered replacement components for SAG & ball mills, vertical roller mills, cement plants, and slurry pumps. Every part manufactured in premium wear-resistant alloys with exact OEM dimensional compatibility. From mill liners to pump impellers—we supply the critical components that keep high-tonnage operations running.
- 4Equipment Categories
- 500+Part Models Available
- 100%OEM Compatible
- 35+Years Manufacturing
Mission-Critical Components for Continuous Operations
Equipment downtime in mining and cement operations costs $15,000-50,000 per hour in lost production. ATF supplies precision-engineered replacement components that extend service intervals, reduce emergency shutdowns, and lower total cost of ownership across your entire processing circuit—from primary grinding through final product discharge.
20-40% Longer Service Intervals
Advanced metallurgy and optimized component profiles reduce replacement frequency. SAG mill liners achieving 11,000+ hours vs 8,500-hour industry average. Lower maintenance costs and fewer production interruptions.
Zero Modification Required
Reverse-engineered to OEM specifications with ±0.5mm tolerance verification. Compatible with Metso, FLSmidth, Polysius, Warman, and 50+ major equipment brands. Installation using existing mounting hardware.
Application Engineering Assistance
Technical consultation for material selection, wear rate analysis, and performance optimization. Field-proven recommendations based on 35+ years supplying global mining and cement operations.
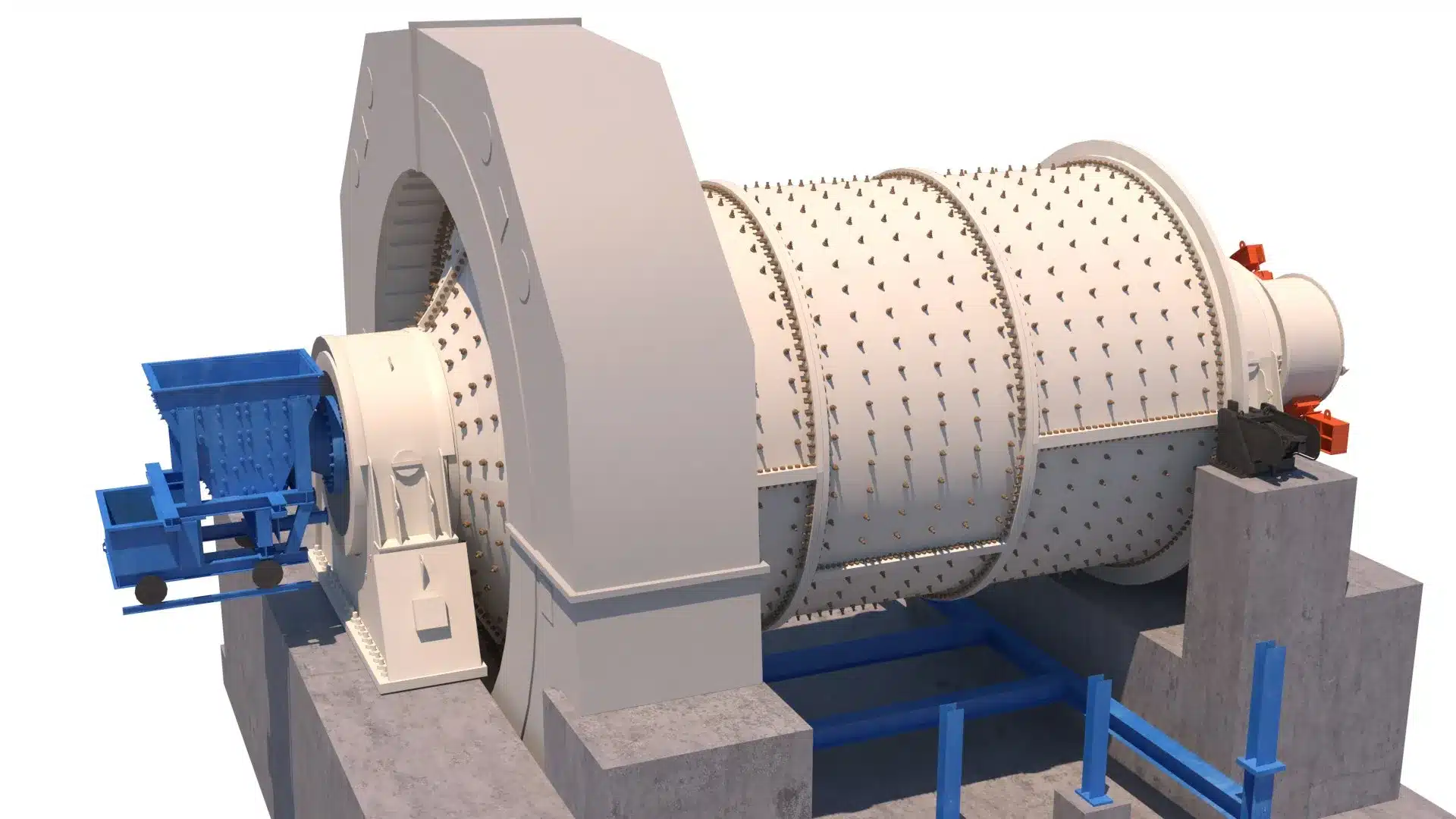
SAG & Ball Mill Spare Parts
High-impact wear components for primary and secondary milling circuits processing gold, copper, iron ore, platinum, and base metals. Chrome-moly shell liners, grinding media, and drive assemblies engineered for 24/7 continuous operation at mill speeds 72-85% critical.

Maximum Availability in High-Tonnage Mills
Complete liner systems, lifter bars, discharge grates, grinding media, and drive components for SAG mills 18-40 ft diameter and ball mills 12-28 ft. Materials selection based on ore work index (Wi 8-22 kWh/t), abrasiveness index (Ai), and mill operating parameters to maximize service life while maintaining grinding efficiency.
Available Components:
- Shell & End Liners: Hi-Lo wave, Hi-Hi stepped profiles in chrome-moly steel (1.5-3.0% Cr, 0.5-1.0% Mo). Hardness HB 400-480 as-cast.
- Lifter Bars & Grates: Radial and spiral lifter designs optimized for charge trajectory. Discharge grates in multiple open area percentages (8-15%).
- Hybrid Liner Systems: Poly-Met™ composite designs combining metallic impact zones with rubber damping sections. 50% weight reduction vs full metallic.
- Grinding Media: Forged steel balls (HRC 58-65 surface) 75-150mm SAG, low-chrome cast balls (HRC 55-63) 25-100mm for ball mills.
- Drive Components: Pinion gears, girth gears (typically 4-8m diameter), trunnion bearings, and thrust assemblies for mills 2,000-8,000 kW.
Hybrid Rubber-Metal
Poly-Met™ Composite
Forged Media
Application-Specific Selection:
Critical Selection Factors:
- Ore Characteristics: Work Index (Wi), Bond Abrasion Index (Ai), and feed size distribution (F80) determine optimal liner material and profile geometry
- Mill Operating Parameters: Speed (% critical), volumetric loading (25-35% typical), and power draw affect liner wear patterns and service life
- Circuit Configuration: SAG-Ball vs single-stage SAG, pebble crusher integration, and screen apertures influence media size selection
Vertical Roller Mill (VRM) Components
Abrasion-resistant castings for fine grinding applications in cement raw material preparation, coal pulverization, slag processing, and industrial minerals. High-chrome rollers, table segments, and separator internals designed for continuous operation at grinding pressures 50-150 MPa producing fineness 3,000-5,000 cm²/g Blaine.
Consistent Product Fineness & Predictable Wear Rates
Precision-ground rollers, modular table segments, nozzle ring assemblies, wear plates, separator internals, and hydraulic system components for Loesche, Pfeiffer, FLSmidth ATOX, Polysius, and KHD vertical mills. Material grades optimized for fine-particle abrasion resistance while maintaining dimensional stability under hydraulic loads 800-3,000 kN per roller.
Core VRM Components:
- Grinding Rollers: High-chrome white iron castings (15-28% Cr) with optional hardfaced overlay. Standard profiles: convex, flat, concave based on material characteristics. Hardness HRC 58-64 matrix.
- Table Segments: Modular bolt-in designs for rapid replacement. High-chrome castings with integrated hardfacing in high-wear zones. Segment sizes matched to mill diameter 1.5-6.5m.
- Nozzle Rings: Precision-cast air distribution assemblies with optimized vane angles. Replaceable vane inserts extend service life 20-30% vs monolithic designs.
- Wear Protection: High-chrome white iron plates for mill housing, chute liners, and classifier housing. Modular designs minimize replacement area and downtime.
- Separator Components: Dynamic classifier rotor cages, guide vanes, and housing liners. Materials selected for erosion resistance in high-velocity (20-30 m/s) particle-laden air streams.
- Hydraulic Assemblies: Cylinders, accumulators, seals for grinding pressure control systems. Compatible with nitrogen pre-charge systems 70-80% operating pressure.
Hardfaced Overlays
Ni-Hard Variants
In-Situ Repair
Material-Specific Applications:
Performance Optimization Strategies:
- Roller Profile Management: Laser measurement systems track wear patterns. Re-profiling at 10-15mm wear depth restores grinding geometry and efficiency. In-situ hardfacing extends life 30-50% vs replacement.
- Grinding Pressure Optimization: Balance throughput requirements against wear rates. Each 10 MPa pressure reduction typically extends roller life 8-12% while reducing specific energy 2-4 kWh/ton.
- Preventive Hardfacing: Scheduled overlay welding before critical wear depth reached. Chromium carbide or tungsten carbide deposits depending on application severity and economic analysis.
Cement Plant High-Temperature Components
Heat-resistant alloys and refractory-backed assemblies for rotary kilns, preheater/calciner systems, clinker coolers, and auxiliary equipment. Components engineered for thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and mechanical integrity at operating temperatures 850-1,450°C in continuous duty cycles 330+ days per year.

Thermal Cycling Resistance & Extended Service Life
Rotary kiln mechanical assemblies, preheater/calciner castings, clinker cooler grates, sealing systems, support rollers, tyres, and process equipment designed for cement production 1,500-10,000 TPD capacity. Material selection addresses thermal shock, oxidation/carburization, and mechanical loading in temperature zones 200-1,450°C.
Critical High-Temperature Parts:
- Rotary Kiln Components: Refractory anchor systems, girth gears (4-8m diameter, 200-400mm face width), drive assemblies, support rollers (600-1,200mm diameter). Kiln tyres in normalized/quenched & tempered alloy steel.
- Preheater/Calciner Internals: Cyclone liner castings in HK series stainless (25% Cr, 20% Ni) for 800-950°C service. Riser ducts, tertiary air ducts, and calciner refractory anchors. Maximum service temperature 1,000-1,100°C.
- Clinker Cooler Assemblies: Reciprocating grate coolers most common—mobile and stationary grate castings. Hot zone (900-1,200°C) requires HK40 heat-resistant stainless. Transition and cool zones use high-chrome iron or lower-grade alloys.
- Sealing Systems: Kiln inlet/outlet end seals (contact and non-contact types), preheater expansion joint seals, cooler seals. Materials: graphite-impregnated fabric, high-temperature ceramics, spring-loaded plate assemblies.
- Rotating Elements: Kiln support rollers with water-cooled shafts, thrust rollers, trunnion assemblies. Precision machining required—radial runout <0.5mm to prevent shell ovality and uneven refractory wear.
Heat-Resistant Alloys
High-Chrome Grates
Refractory Systems
Temperature Zone Requirements:
Critical Selection Considerations:
- Fuel Type Impact: Alternative fuels (waste-derived, biomass) affect gas chemistry and ash composition. Higher sulfur and chloride content accelerates corrosion—may require upgraded materials or protective coatings.
- Thermal Cycling: Start-stop frequency determines thermal shock requirements. Plants with frequent shutdowns require materials with enhanced thermal cycling resistance and slower heating/cooling ramp rates.
- Raw Mix Chemistry: High alkali content in raw materials increases coating build-up and refractory attack. Influences refractory selection and kiln operating parameters (speed, feed rate, flame profile).
Slurry Pump Wet-End Components
Abrasion-resistant impellers, liners, and seal assemblies for centrifugal slurry pumps handling high-solids content (15-65% by weight) in tailings transport, dewatering, hydrocyclone feed, flotation circuits, and dredging applications. Components designed for particle sizes d50 20-500µm at pump speeds 400-1,200 RPM delivering heads 15-120 meters.

Severe Abrasion Performance in Particle-Laden Slurries
High-chrome iron impellers (A05, A49 grades), volute liners, throat bushes, frame plate liners, expellers, stuffing boxes, and mechanical seal assemblies for horizontal and vertical slurry pumps. Material selection based on particle characteristics (size, shape, hardness), slurry velocity (2-6 m/s), and corrosion environment (pH 4-12 typical).
Essential Wet-End Components:
- Impellers (Closed, Semi-Open, Open): A05 high-chrome iron (26-30% Cr, HB 600-700) for coarse, angular particles. A49 premium grade (28-32% Cr) for most severe duty. Rubber-lined impellers for fine, non-sharp slurries. Vane profiles optimized for efficiency vs wear resistance trade-off.
- Volute Liners (Casing Liners): Replaceable wear sections bolt into pump casing. High-chrome iron most common—allows quick changeout vs full casing replacement. Rubber variants available for fine-particle applications where resilience reduces wear.
- Throat Bushes (Suction Liners): Critical wear component at impeller eye inlet. High-chrome iron standard—wear indicates operation away from best efficiency point (BEP) or recirculation issues. Rapid wear suggests pump oversized for duty or inadequate NPSH.
- Frame Plate Liners (Wear Plates): Protect pump casing from internal recirculation flow patterns. Bolt-in replaceable design. High-chrome iron or rubber depending on particle characteristics and pump design.
- Expellers (Shaft Protection): Front and rear sealing protection preventing slurry ingress to bearing housing. Typically high-chrome iron or alloy steel. Critical for mechanical seal life—inadequate expeller clearance allows particle intrusion.
- Mechanical Seal Assemblies: Single or double mechanical seals with seal water flush systems. Seal water pressure must exceed pump discharge by 70-140 kPa. Filtration <10µm critical. Seal face materials: silicon carbide vs silicon carbide most common for abrasive slurries.
A49 Premium 28-32% Cr
R55 Natural Rubber
Ni-Hard Variants
Application-Specific Material Selection:
Critical Performance Factors:
- Particle Characteristics: Size (d50, d85) determines primary wear mechanism. Sharp, angular particles cause cutting wear—require metal components. Rounded particles cause sliding wear—rubber often superior to metal in this regime.
- Slurry Velocity: Wear rate proportional to velocity raised to power 2.5-3.5. Reducing velocity from 5 m/s to 4 m/s can extend life 40-50%. Achieved through larger pipe diameters or reduced pump speeds—must balance against capital costs.
- Operating Point: Pumps must operate near BEP (typically 80-110% design flow). Operation far from BEP causes recirculation, excessive throat bush wear, and premature seal failure. Pump curve testing recommended annually to track performance degradation.
Materials & Metallurgy — Engineering Selection Guide
Optimal material performance requires matching alloy properties to application duty: impact severity, abrasiveness index, operating temperature, corrosive environment, and mechanical loading. Below are the primary material families with specific chemistry, hardness ranges, and optimal duty conditions based on field experience across 1,000+ installations.
Chrome-Moly Steel & Hybrid Mill Liners
Low-alloy steel castings optimized for impact-dominated grinding applications. Chemistry: 1.5-3.0% Cr, 0.5-1.0% Mo, 0.5-0.7% C provides combination of toughness (impact resistance) and hardness (abrasion resistance). Normalized and tempered heat treatment develops optimal microstructure.
- Full Metallic Liners: Traditional design for high-tonnage SAG mills. Best wear life in competent ores (Wi 14-18 kWh/t). Liner consumption 0.9-1.3 kg/ton ore milled typical.
- Poly-Met™ Composite: Metallic impact face with elastomer backing layer. 50% weight reduction enables faster liner changes (8-12 hours vs 18-24 hours). Reduces mill downtime 30-40% during liner replacement cycles.
- Full Rubber Liners: Fine grinding ball mills, secondary/tertiary duty. Natural rubber (Shore A 65-75) provides excellent abrasion resistance with low noise. Not suitable for coarse ore or SAG mills (insufficient impact resistance).
Field data: Service life 8,000-12,000 hours SAG mills | 6,000-9,000 hours ball mills | Varies with ore hardness (Wi), abrasiveness (Ai), and mill operating parameters (speed, charge volume)
High-Chrome White Iron (VRM Components)
Carbide-rich iron castings for fine-particle abrasion with controlled impact. Hypoeutectic composition (15-28% Cr) develops chromium carbide (M7C3) in martensitic matrix. Carbides provide abrasion resistance, matrix provides toughness. Heat treatment adjusts carbide morphology and matrix hardness.
- Standard As-Cast High-Chrome: 18-23% Cr most common for raw material VRM grinding. Provides 12,000-18,000 hour roller life at 90-110 MPa grinding pressure. Cost-effective for moderate abrasion applications.
- Hardfaced Overlay (Chromium Carbide): Base casting overlaid with 12-20mm weld deposit. Extends life 30-50% in severe abrasion (slag grinding, petcoke). Overlay chemistry: 25-32% Cr, 3-5% C. Hardness HRC 60-68 overlay zone.
- In-Situ Hardfacing Repair: Worn surfaces rebuilt on-site during scheduled shutdowns. Restores roller profile geometry and extends life additional cycle. Typical at 10-15mm wear depth before base metal exposure. Requires preheat 200-250°C and controlled cooling.
Wear performance: As-cast rollers 8,000-15,000 hours | Hardfaced rollers 12,000-22,000 hours | Table segments 12,000-20,000 hours | Nozzle rings 15,000-25,000 hours in cement raw material grinding
Heat-Resistant Cast Stainless (HK Series)
Austenitic stainless steel castings for elevated temperature service with thermal cycling. High chromium (23-27%) provides oxidation resistance, high nickel (18-22%) stabilizes austenite structure and prevents sigma phase formation. Carbon content 0.35-0.55% forms carbides at grain boundaries for creep resistance.
- Preheater Cyclone Liners: Operating temperature 800-950°C with moderate thermal cycling. HK40 standard grade—superior to carbon steel which oxidizes rapidly >650°C. Service life 3-5 years vs 12-18 months for carbon/low-alloy steel in this duty.
- Cooler Grates (Hot Zone): Most demanding application—temperatures 900-1,200°C with severe thermal cycling during starts/stops. HK40 or HP (35Cr-45Ni) required. Grate life 12-24 months. Thermal shock resistance critical—rapid temperature changes cause cracking in lower-grade materials.
- Kiln Inlet Components: Transition from refractory-lined kiln to metal preheater structure. Temperature 900-1,000°C. Oxidation resistance primary concern—chrome oxide surface layer forms protective scale. Carburization resistance important in reducing atmospheres.
Material selection: HK40 most common (good balance cost/performance) | HP grade for most severe thermal cycling | HT grade (15Cr-35Ni) intermediate cost option for 850-950°C service
High-Chrome Iron & Rubber (Slurry Pumps)
Material selection based on particle characteristics determines pump wear life. Coarse, angular particles cause cutting/gouging wear—require hard, carbide-rich metal. Fine, rounded particles cause sliding/erosion wear—resilient rubber often outperforms metal through energy absorption mechanism rather than hardness.
- A05 High-Chrome Iron: Industry standard for coarse tailings transport (d50 >100µm). Best performance in angular particles (crushed rock, mine tailings). Service life 2,000-4,000 hours impellers, 3,000-6,000 hours volute liners. Wear rate proportional to slurry velocity³.
- A49 Premium Grade: Enhanced chemistry 28-32% Cr with controlled carbide size/distribution. 25-40% longer life than A05 in most severe applications (high velocity, large particle size, high hardness). Economics favor A49 when pump changeout costs high (remote locations, difficult access).
- R55 Natural Rubber: Superior to metal in fine slurries (d50 <75µm) with rounded particle morphology. Elastomer deforms under particle impact, absorbing energy. Life 4,000-8,000 hours in suitable applications—2x metal equivalent. Not suitable for coarse, sharp particles or high temperatures (>60°C degrades rubber).
Selection methodology: Particle size d50 primary factor | Particle shape (angularity) determines metal vs rubber | Slurry velocity affects both materials (reduce velocity = extend life) | pH and temperature influence rubber performance
High-Chrome White Iron (ASTM A532) & Ni-Hard
Carbide-rich white irons for severe abrasion with moderate impact. ASTM A532 classification based on chrome content: Class I (12-18% Cr), Class II (18-23% Cr), Class III (23-30% Cr). Higher chrome = more carbides = better abrasion resistance but lower impact toughness. Ni-Hard family adds nickel (3-5%) for enhanced toughness vs straight high-chrome.
- A532 Class I (12-18% Cr): Lowest cost high-chrome grade. Moderate abrasion resistance. Used in light-duty chute liners, screen plate backing. Hardness HRC 56-60. Less brittle than higher chrome grades—better impact tolerance.
- A532 Class II (18-23% Cr): Most common grade for wear applications. Good balance abrasion resistance vs cost. Chute liners, bin liners, wear plates in mineral processing plants. Hardness HRC 58-63. Industry workhorse material.
- A532 Class III (23-30% Cr): Maximum abrasion resistance in white iron family. Used in most severe sliding abrasion with minimal impact. Hardness HRC 60-66. Brittle—prone to cracking if impact present. Typically backed with ductile iron or mild steel for shock absorption.
- Ni-Hard (3-5% Ni, 1.5-4% Cr): Lower cost alternative to high-chrome where extreme abrasion resistance not required. Better machinability than high-chrome. Hardness HRC 50-58. Good for moderate abrasion with some impact present.
Application note: High-chrome white irons require careful installation—brittle nature means bolt holes must be precisely located, bolts properly torqued (avoid over-tightening), and thermal expansion accommodated in design
Forged & Cast Steel Balls
Grinding media selection based on mill type, ore characteristics, and economic optimization. Forged steel provides superior toughness for high-impact SAG mills. Low-chrome and high-chrome cast balls offer cost-performance alternatives for ball mills where impact is lower and abrasion dominates. Media cost typically 15-30% of total grinding costs.
- Forged Steel Balls (SAG Mills): High-impact resistance essential for SAG mill duty. Hardness gradient (hard surface, tough core) resists breakage. Sizes 75-150mm diameter typical. Consumption rate 0.5-1.2 kg/ton ore depending on ore hardness and mill design. Premium product—costs 30-50% more than cast balls.
- Low-Chrome Cast Balls (Ball Mills): Cost-effective media for secondary/tertiary ball mills. Chemistry 0.6-1.2% Cr. Hardness HRC 55-63. Balanced performance in abrasion and moderate impact. Sizes 25-60mm most common. Consumption 0.3-0.8 kg/ton in typical regrind duty. Best economics for high-tonnage operations.
- High-Chrome Cast Balls (Severe Abrasion): Chemistry 1.5-3.2% Cr provides enhanced abrasion resistance. Hardness HRC 60-66. Used in highly abrasive ores where wear life justifies higher media cost. More brittle than low-chrome—higher breakage rate in high-impact applications. Sizes 25-50mm typical for fine grinding.
Media optimization: Larger balls (>80mm) for coarse grinding, smaller balls (<40mm) for fine grinding | Ball size distribution affects grinding efficiency and energy consumption | Monitor mill charge by weight and top size—maintain optimal ball size distribution for ore characteristics
Engineering Support for Material Selection
Selecting optimal materials requires analysis of multiple interacting factors: ore/material characteristics (PSD, hardness, mineralogy), operating conditions (temperature, pH, impact severity), equipment parameters (mill speed, grinding pressure, pump velocity), and economic constraints (capital vs operating cost trade-offs). Share your application details—our metallurgical engineers provide specific material recommendations with predicted service life and cost-per-ton analysis.
Component Gallery — Installation & Wear Patterns
Representative photographs showing typical components, installation configurations, wear patterns at replacement intervals, and material variations across SAG/ball mills, vertical roller mills, cement plant equipment, and slurry pump assemblies.