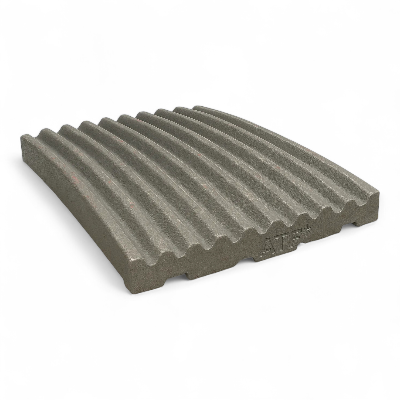
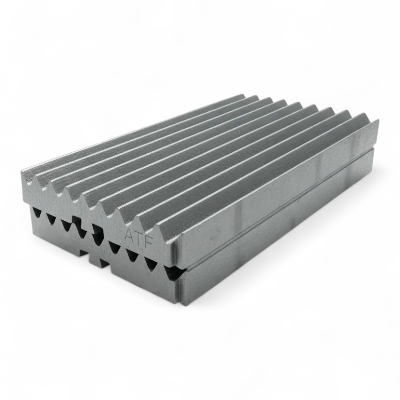
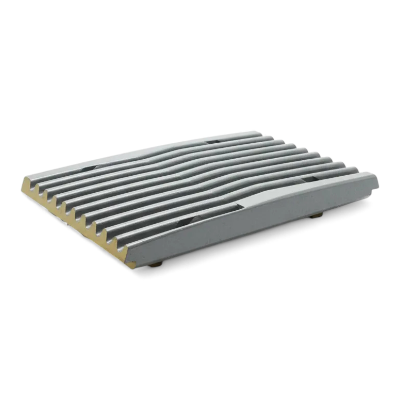
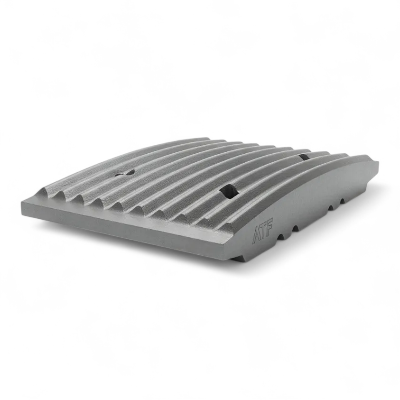
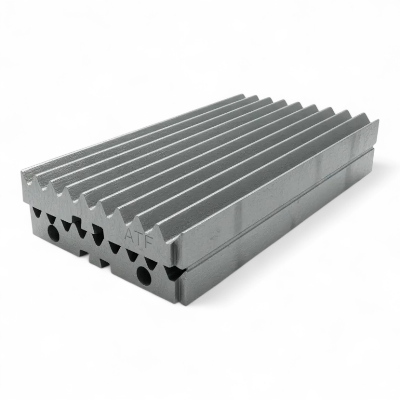
Jaw Plates: Mn13-Mn22 Manganese Steel with TiC Insert Options
Jaw plates (jaw dies) engineered in Mn13–Mn22 austenitic manganese with optional TiC inserts deliver 40-100% longer wear life in abrasive applications. We manufacture fixed jaw plates, movable jaw plates (swing jaw), and stationary jaw plates compatible with Metso C-Series, Sandvik CJ/QJ, Terex Finlay J-Series, Powerscreen Premiertrak, Kleemann MC, and 50+ brands. Aftermarket jaw plates for sale with superior wear life—optimized tooth profiles for aggregate, mining, recycling, and cement duty to reduce jaw plate cost per ton, stabilize gradation, and extend change-out intervals. ISO 9001 certified manufacturing with 35+ years experience.
- 35+Years Experience
- 500+Global Customers
- 50+Countries Served
Jaw Plate Materials & Insert Options
Select the optimal metallurgy tuned for your duty and chamber. Each option includes practical application guidance based on 35+ years of field experience.

Manganese 13% — Standard Austenitic
Baseline austenitic manganese steel — work-hardens under impact for surface hardness.
Hardness: HB 180-220 (work-hardens to HB 500+)
Chemistry: C 1.1-1.4%, Mn 11-14%, Cr 1.7-2.3% (ASTM A128 Grade C)
Impact Strength: 150-200 J/cm²
Typical Life: 100,000 tons in medium-duty limestone

Manganese 18% — Industry Standard
Most popular quarry grade — optimal balance of wear life and toughness for general crushing.
Hardness: HB 200-240 (work-hardens to HB 550+)
Chemistry: C 1.1-1.4%, Mn 17-19%, Cr 1.7-2.3%
Impact Strength: 180-250 J/cm²
Typical Life: 130,000 tons (20-35% longer than Mn13)

Manganese 22% — Maximum Toughness
Highest work-hardening threshold for hard, abrasive rock in severe impact conditions.
Hardness: HB 210-250 (work-hardens to HB 600+)
Chemistry: C 1.1-1.4%, Mn 20-24%, Cr 1.7-2.3%
Impact Strength: 200-300 J/cm²
Typical Life: 140,000-185,000 tons in primary duty

Manganese with TiC Inserts — Edge-Reinforced Technology
TiC rods strategically placed at tooth tips/edges resist micro-chipping and slow rounding for extended grip retention.
Matrix Hardness: HB 200-240 (Mn18 base)
TiC Hardness: HV 3200 (ceramic grade — harder than tungsten carbide)
Impact Strength: 180-250 J/cm² (matrix)
Life Improvement: 40-100% longer vs standard Mn13 in suitable applications
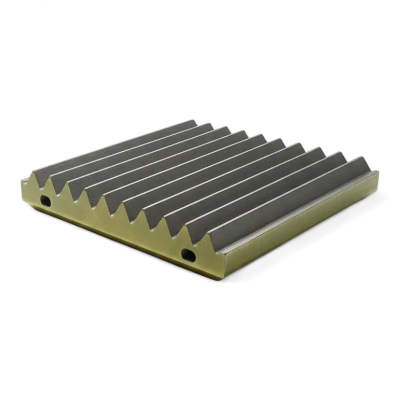
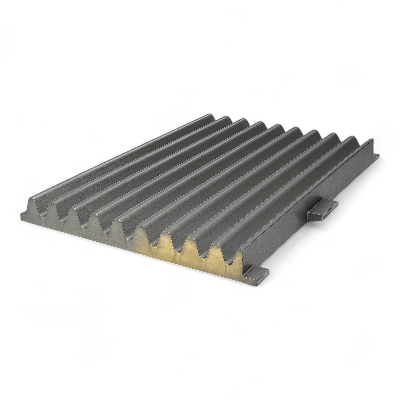
Jaw Plate Gallery: Materials & Manufacturing
ISO 9001 certified foundry with precision casting, solution heat treatment, water quench, CNC machining, and comprehensive QC documentation. 8,000 ton annual capacity with pattern library of 500+ jaw crusher models.
Jaw Plate Wear Science & Metallurgy
Understanding jaw plate wear mechanisms guides material selection. Manganese steel’s unique work-hardening behavior determines how well your plates resist gouging, abrasion, and tooth rounding—directly affecting service life and cost per ton.
Work-Hardening Mechanics
Austenitic manganese steel transforms under impact—the surface layer hardens to HB 500-600+ while the core remains tough (HB 200-250). This creates a wear-resistant shell backed by ductile support. Without sufficient impact energy, work-hardening won’t activate and premature wear results.
Field tip: Maintain choke feed to ensure consistent impact loading. Starved feed creates peening damage rather than proper work-hardening.
Tooth Profile Selection
Tooth geometry affects material grip, fines production, and wear pattern. Common profiles include:
- Corrugated: Standard quarry profile—good balance of grip and wear life
- Deep Tooth: Aggressive bite for primary crushing of large feed
- Super Grip: Enhanced penetration for hard, smooth-faced rock
- Flat: Minimal fines production for specific gradation targets
- Recycling: Reinforced roots to handle rebar and tramp metal
CSS & Nip Angle Effects
Closed Side Setting (CSS) directly impacts wear rate—tighter settings accelerate wear due to increased fines generation. Typical CSS drift of 5-10% indicates approaching change-out time.
Nip angle (typically 18-22°) affects material grip. Out-of-spec angles cause slippage and tooth surface polishing instead of crushing.
Field tip: Use the largest CSS that meets your product specification to maximize jaw plate life.
Abrasion vs. Impact Balance
Jaw plates experience combined abrasion (surface sliding) and impact (compression crushing). Material selection depends on the dominant wear mode:
- High impact, low abrasion: Mn13-Mn18 with good work-hardening response
- High abrasion, moderate impact: Mn18 + TiC inserts at tooth edges
- Severe impact + abrasion: Mn22 with TiC for maximum protection
Heat Treatment Critical Path
Proper heat treatment is non-negotiable for manganese steel performance:
- Solution treatment: 1050-1100°C to dissolve carbides into austenite
- Water quench: Rapid cooling (within 30 seconds) to retain austenitic structure
- Carbide precipitation: Slow cooling or delayed quench causes grain boundary carbides—#1 cause of premature cracking
ATF maintains strict furnace controls and documented quench times on every batch.
Cost-Per-Ton Optimization
True jaw plate economics require lifecycle analysis, not just purchase price:
Cost per ton = (Plate cost + Changeout cost) ÷ Tons processed
Higher-grade materials (Mn18, TiC) often deliver 15-25% lower cost per ton despite 20-45% higher initial price through extended service life and reduced downtime.
Field tip: Track tonnage between changeouts—most operations underestimate extended wear life value.
Decision Matrix: Selecting Optimal Jaw Plates for Your Operation
Utilize our expert matrix to quickly identify the optimal jaw plate metallurgy for your specific application. For personalized recommendations, Request a Technical Review.
Hard Rock Quarrying (Granite, Basalt, Gneiss)
Start: Mn18 with Super Grip profile for optimal work-hardening. → Upgrade: Mn22 for extreme impact or Mn18 + TiC for high-silica content (>65%).
Prioritize higher Mn grades for sufficient impact to activate work-hardening. Expected life: 130,000-185,000 tons. Ideal for Metso C120 jaw plates and similar large primary crushers.
Limestone & Soft Rock (Dolomite, Chalk)
Start: Mn13 with Corrugated profile for cost economy. → Upgrade: Mn18 for higher throughput or extended change-out intervals.
Mn13 cost-effective when impact energy is moderate. TiC generally not required. Expected life: 100,000-140,000 tons. Common in Sandvik CJ412 jaw plates applications.
Concrete Recycling / C&D Waste (Moderate Rebar)
Start: Mn18 with Recycling profile (reinforced roots) for tramp metal tolerance. → Avoid: TiC inserts—tramp steel risk damages ceramic.
Steel-tolerant profile essential; magnetic separation recommended upstream. Expected life: 80,000-120,000 tons (varies with steel content). Typical for Kleemann MC 110 aftermarket jaw plates.
Mining Primary Crushing (Iron Ore, Copper, Gold)
Start: Mn22 with Deep Tooth profile for maximum toughness. → Add: TiC inserts for abrasive ore bodies with controlled steel.
Maximum toughness for large feed and severe impact; proper choke feed critical. Expected life: 150,000-200,000 tons. Engineered for Metso C140 jaw plates and heavy-duty mining applications.
Aggregate Production (Mixed Aggregate, River Gravel)
Start: Mn18 with Corrugated or Super Grip profile. → Optional: TiC for abrasive feeds requiring extended life.
Balance of wear life and product shape; CSS management for spec compliance. Expected life: 120,000-160,000 tons. Popular in QJ341 aftermarket jaw plates.
Cement Raw Materials (Limestone, Clay, Shale)
Start: Mn13-Mn18 with standard Corrugated profile. → Consider: TiC only for high-silica limestone.
Continuous duty demands reliability; consistent sizing for kiln feed optimization. Expected life: 100,000-140,000 tons.
Why TiC-Reinforced Jaw Plates Deliver Quantifiable 40-100% Life Extension
Titanium carbide inserts extend jaw plate service life by protecting the areas that wear fastest—tooth tips and edges. When applied correctly, TiC delivers measurable cost-per-ton savings.
Edge Protection Where It Matters
TiC inserts (HV 3200) are strategically placed at tooth tips and leading edges—the areas experiencing highest abrasive contact. This slows the rounding process that degrades crushing efficiency and widens CSS.
Result: Stable CSS for longer periods, more consistent product gradation, fewer mid-campaign adjustments.
40-100% Extended Wear Life
In suitable applications (abrasive feeds with moderate impact), TiC-reinforced jaw plates consistently deliver 40-100% longer service life compared to standard Mn13.
Documented performance: 185,000+ tons in granite applications where standard Mn13 achieved 100,000 tons.
Lower Cost Per Ton
Despite 35-45% higher initial cost, TiC jaw plates typically deliver 15-20% lower cost per ton through extended life and reduced changeout frequency.
Example calculation: Mn13 at $5,000/100K tons = $0.050/ton. TiC at $7,250/185K tons = $0.039/ton (22% savings).
When TiC Makes Sense
- Tooth edges round too fast in current application
- CSS drift is excessive between changeouts
- Operations tracking cost-per-ton rather than purchase price
- Abrasive feeds (high silica granite, quartzite)
- Good steel control upstream (no uncontrolled tramp metal)
Avoid TiC if: Frequent tramp steel, severe misalignment, very soft feeds where Mn13 is adequate.
Precision-Engineered Jaw Plates Compatible with Leading Crusher Brands
ATF designs, engineers, and stocks high-performance jaw plates for the most popular jaw crushers worldwide. Select your crusher brand below to view supported models and compatible Mn grade options, including specialized aftermarket jaw plates for Metso C-Series and Sandvik CJ/QJ wear parts equivalent.
Metso (Nordberg) – C-Series
- C80
- C96 (Aftermarket jaw plates for C96)
- C100
- C106 (Aftermarket jaw plates for C106)
- C110
- C116
- C120 (Aftermarket jaw plates for C120)
- C130
- C140
- C150
- C160
- C200
- LT96
- LT106
- LT116
- LT120
- LT140
Sandvik – CJ/QJ/UJ Series
- CJ211
- CJ411
- CJ412 (Sandvik CJ412 wear parts equivalent)
- CJ612
- CJ613
- CJ615
- CJ815
- QJ241
- QJ341 (Aftermarket jaw plates for QJ341)
- QJ441
- UJ310
- UJ440i
Terex Finlay – J-Series
- J-960
- J-1160
- J-1170
- J-1175 (Aftermarket jaw plates for J-1175)
- J-1480
Powerscreen – Premiertrak
- Premiertrak 300
- Premiertrak 400 (Aftermarket Premiertrak 400 jaw plates)
- Premiertrak 400X
- Premiertrak 600
- Metrotrak
Kleemann – MC Series
- MC 100
- MC 110 (Aftermarket Kleemann MC 110 jaw plates)
- MC 120
- MC 125
- MC 140
McCloskey – J Series
- J35
- J40 (Aftermarket J40 jaw plates)
- J45
- J50 (Aftermarket J50 jaw plates)
Telsmith – Jaw Crushers
- 2036
- 2550
- 3042
- 3244
- 4248
Komatsu – BR Series
- BR380JG
- BR550JG
- BR580JG
Don’t see your exact jaw crusher model or need a custom solution? ATF proudly supports over 500 OEM specifications, including various legacy variants. Request a custom quote with your make/model and original part reference to confirm if we can supply high-performance jaw plates, including advanced TiC insert options, engineered specifically for your needs.
Installation & Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and operational practices can extend jaw plate life by 25-40%. These field-proven guidelines help maximize your investment.
Pre-Installation Inspection
Before installing new jaw plates:
- Inspect frame seating surfaces for damage or debris buildup
- Verify wedge blocks and backing plates are in good condition
- Check toggle plate, toggle seat, and pitman bearing for wear
- Clean all mating surfaces thoroughly
- Verify new plates match dimensional specifications (±2mm)
Proper Torque & Seating
Correct bolt torque prevents plate movement and premature wear:
- Follow OEM torque specifications (typically 800-1200 Nm)
- Use calibrated torque wrenches—not impact guns for final torque
- Apply anti-seize compound to bolt threads
- Re-torque after first 8 hours of operation
- Check torque weekly during break-in period
Choke Feed Management
Proper choke feed is critical for work-hardening activation:
- Maintain consistent feed level above toggle plate height
- Avoid surge feeding—causes peening damage
- Prevent bridging in feed hopper
- Use vibrating grizzly feeders for consistent delivery
- Monitor amperage draw for feed consistency
CSS Monitoring & Adjustment
Regular CSS monitoring extends jaw plate life:
- Measure CSS daily using lead ball or electronic measurement
- Document readings to track wear progression
- Adjust shims to maintain target CSS as plates wear
- Plan changeout when CSS drift exceeds 10%
- Consider plate flip at 50-60% wear to extend total life
Flip Procedure for Extended Life
Flipping jaw plates at proper timing can extend total life by 40-60%:
- When to flip: At 50-60% wear or when CSS drift reaches 5-8%
- Orientation: Rotate 180° (top-to-bottom), not side-to-side
- Both plates: Flip fixed and movable jaw simultaneously
- Expected benefit: Second half achieves 70-85% of first half life
- Not all profiles: Verify flip compatibility with your tooth design
Storage & Handling
Proper storage protects your investment:
- Store flat on wooden pallets—never stack directly on concrete
- Protect from direct weather exposure
- Apply rust preventative to machined surfaces
- Use proper lifting equipment—jaw plates are heavy (500-3000+ kg)
- Never drop or drag jaw plates—manganese is brittle before work-hardening
✓ DO
- Maintain consistent choke feed
- Monitor CSS daily and document readings
- Re-torque bolts after break-in
- Flip plates at 50-60% wear
- Replace cheek plates when worn
- Use calibrated torque tools
✗ AVOID
- Running CSS tighter than necessary
- Starved or surge feeding
- Ignoring toggle plate wear
- Dropping plates during installation
- Operating beyond minimum thickness
- Mixing mismatched Mn grades
Jaw Plate Service Life Data by Application
Real-world performance data from customer installations. Results vary based on feed characteristics, CSS settings, and operational practices.
| Application | Feed Material | Crusher Type | Mn13 Life | Mn18 Life | Mn18+TiC Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Quarry | Granite (UCS 180 MPa) | Metso C120 | 100,000 t | 135,000 t | 175,000 t |
| Primary Quarry | Basalt (UCS 200 MPa) | Sandvik CJ613 | 95,000 t | 130,000 t | 165,000 t |
| Limestone Quarry | Limestone (UCS 80 MPa) | Metso C96 | 140,000 t | 165,000 t | N/A* |
| Concrete Recycling | Demolished concrete | Kleemann MC 110 | 80,000 t | 110,000 t | N/A** |
| Mining Primary | Iron ore (UCS 160 MPa) | Terex J-1175 | 85,000 t | 120,000 t | 155,000 t |
| Mining Primary | Copper ore (UCS 140 MPa) | Metso C140 | 90,000 t | 125,000 t | 160,000 t |
| Aggregate Production | River gravel | Sandvik QJ341 | 120,000 t | 150,000 t | 180,000 t |
| Cement Raw Material | Limestone + clay | Metso C110 | 130,000 t | 160,000 t | N/A* |
*TiC not recommended for soft feeds where standard Mn is more economical. **TiC not recommended due to tramp steel risk in recycling applications. All figures represent typical performance; actual results depend on feed conditions, CSS, and operational practices.
Jaw Plate Troubleshooting Guide
Diagnose common jaw plate wear problems and implement corrective actions to extend service life.
🔴 Premature Tooth Rounding
- Mn grade too low for feed abrasiveness
- Insufficient impact for work-hardening (starved feed)
- High silica content in feed material
- Upgrade to higher Mn grade (Mn18 or Mn22)
- Add TiC inserts at tooth edges
- Improve choke feed consistency
🔴 Surface Cracking/Spalling
- Improper heat treatment (carbide precipitation)
- Severe tramp steel impacts
- Excessive operating temperature
- Welding damage from field repairs
- Verify supplier heat treatment certification
- Improve magnetic separation upstream
- Never weld on manganese plates in the field
- Source from ISO-certified foundries with documented QC
🔴 Uneven Wear Pattern
- Feed chute misalignment directing material to one side
- Worn cheek plates allowing material escape
- Toggle plate or bearing wear causing jaw misalignment
- Adjust feed chute for center delivery
- Replace worn cheek plates
- Inspect and replace toggle components if worn
- Verify jaw frame alignment
🔴 Excessive CSS Drift
- Loose jaw plate mounting bolts
- Worn wedge blocks or backing plates
- Toggle plate wear or improper seating
- Plates approaching end of service life
- Re-torque mounting bolts to specification
- Inspect and replace wedge blocks as needed
- Check toggle plate condition and seating
- Plan changeout if plates are at >70% wear
🔴 Plate Movement/Rattling
- Insufficient bolt torque
- Damaged seating surfaces
- Missing or worn backing plates
- Dimensional mismatch between plate and frame
- Remove plate and inspect seating surfaces
- Apply proper torque with calibrated tools
- Replace damaged backing plates
- Verify plate dimensional specifications (±2mm)
🔴 Tooth Peening/Mushrooming
- Starved feed causing single-particle impacts
- Mn grade too high for impact energy (doesn’t work-harden)
- Running empty or near-empty chamber
- Maintain proper choke feed at all times
- Consider lower Mn grade if impact is insufficient
- Adjust feeder to maintain consistent material flow
- Never run crusher empty
OEM Compatibility: Popular Jaw Crusher Models & Optimized Jaw Plate Materials
Detailed guidance on tooth profile, Mn grade, and insert coverage by model and duty cycle.
| Brand | Model | Typical Duty Profile | Recommended Jaw Plates* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metso | C96 | Medium quarry, contract crushing | Mn18 Corrugated; Mn13 for soft limestone |
| Metso | C106 | Primary quarry | Mn18 Corrugated; Mn18 + TiC for abrasive granite |
| Metso | C120 | High throughput primary | Mn18/Mn22 Super-Grip; TiC option for hard rock |
| Metso | C140 | Large primary mining | Mn22 Deep Tooth; Mn18 + TiC for balanced duty |
| Sandvik | CJ412 | General purpose stationary | Mn18 Corrugated; Recycling profile for C&D |
| Sandvik | CJ613 | High capacity primary | Mn18/Mn22 Super-Grip; TiC for high-silica |
| Sandvik | QJ341 | Mobile quarry/recycling | Mn18 Super-Grip; Mn18 + TiC for harder stone |
| Terex Finlay | J-1175 | Quarry & mining primary | Mn18–Mn22 Deep Tooth; TiC for high silica |
| Powerscreen | Premiertrak 400X | Versatile mobile duty | Mn18 Corrugated; Flat for low-fines targets |
| Kleemann | MC 110 | Aggregate production | Mn18 Quarry tooth; Mn22 for abrasive granite |
| Kleemann | MC 120 | High capacity mobile | Mn18 Super-Grip; TiC for extended life |
| McCloskey | J50 | High capacity primary | Mn22 Super-Grip; Mn18 + TiC as balanced option |
*Selection depends on feed hardness/shape, CSS, nip angle, and steel control. Contact our engineering team for application-specific recommendations.
Industries We Empower with Superior Jaw Plates
Mining & Quarrying
Precision-engineered jaw plates for high-tonnage operations in hard rock mining.
- Optimized for primary & secondary crushing circuits
- Extended service life in demanding conditions
- Mn22 and TiC options for severe duty
Aggregates Production
Optimized jaw plates ensuring consistent product gradation for crushed stone operations.
- Multiple tooth profiles for target gradation
- Stable CSS for specification compliance
- Cost-per-ton optimization focus
Recycling & C&D
Steel-tolerant jaw plates for concrete recycling and demolition waste processing.
- Recycling tooth profiles with reinforced roots
- Mn18 toughness handles occasional rebar
- Reduced downtime from tramp metal
Cement Production
Reliable jaw plates for continuous-duty limestone crushing in cement plants.
- Limestone & cement raw materials
- High-availability requirements
- Extended change-out intervals
What are jaw plates (jaw dies)?
Jaw plates (jaw dies) are the fixed and movable manganese steel liners that crush material against each other in a jaw crusher. The tooth profile and manganese grade determine grip strength, reduction ratio, and wear life.
- Fixed jaw plate: Mounts to the crusher frame and remains stationary
- Movable jaw plate (swing jaw): Attaches to the pitman and creates the crushing action
How do I select the right jaw plates for my crusher?
Consider these key factors:
- Feed material hardness: Mn13 for soft rock, Mn18 for general quarrying, Mn22 for hard/abrasive rock
- Application type: Primary vs. secondary crushing affects tooth profile selection
- CSS requirements: Tighter CSS needs more wear-resistant materials
- Budget vs. lifecycle cost: Calculate cost per ton, not just initial price
Which manganese grade should I choose?
- Mn13: Best for soft rock (limestone) or cost economy priority. Baseline performance.
- Mn18: Most popular — suits most quarry duty, 20-35% longer life than Mn13. Industry standard.
- Mn22: For very hard/abrasive rock with good choke feed. Requires sufficient impact to work-harden.
When should I use TiC inserts?
Use TiC-reinforced jaw plates when tooth edges round too fast in abrasive feeds and impact loading is moderate to high:
- Typical life improvement: 40-100% vs. standard Mn13
- Best for: Hard granite, basalt with high silica content
- Avoid if: Frequent uncontrolled tramp steel (can crack inserts)
Despite 35-45% higher initial cost, TiC usually delivers 15-20% lower cost per ton.
When should I replace jaw plates?
Replace at 70% wear (30% remaining thickness) to protect the crusher frame.
- Small jaws (C96): Replace at 25-30mm remaining
- Medium jaws (C110, C120): Replace at 35-45mm remaining
- Large jaws (C140, C160): Replace at 50-65mm remaining
Also replace when CSS drift exceeds 10% or visible cracks appear.
What causes premature jaw plate wear?
- CSS too tight: Accelerates wear 30-50%
- Poor choke feed: Causes tooth peening
- Tramp steel: Creates divots
- Worn cheek plates: Allow material escape
- Improper torque: Causes plate movement
Addressing these factors can extend life by 25-40%.
What are the best jaw plates for granite?
- Recommended: Mn18 + TiC inserts (160,000-185,000 tons)
- Alternative: Mn22 with Super Grip profile (140,000-165,000 tons)
- Avoid: Standard Mn13 in granite (only 100,000-120,000 tons)
TiC delivers 15-20% lower cost per ton despite higher initial cost.
Can I flip jaw plates to extend life?
Yes, flipping can extend total life by 40-60%:
- When: At 50-60% wear or CSS drift of 5-8%
- How: Rotate 180° (top-to-bottom), both plates simultaneously
- Benefit: Second half achieves 70-85% of first half life
Not all profiles allow flipping — verify compatibility first.
How do CSS and nip angle affect wear?
CSS: Smaller CSS increases fines and accelerates wear. Use largest CSS that meets product spec.
Nip angle: Optimal 18-22°. Out-of-spec causes slippage and tooth polishing.
Monitor CSS drift — 5-10% drift indicates time for replacement or flip.
Do I need to replace cheek plates with jaw plates?
Inspect cheek plates during every jaw plate change-out. Replace if worn beyond 50% thickness.
Severe cheek wear accelerates jaw plate wear, creates uneven loading, and reduces chamber efficiency. Replace as matched sets when possible.
What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket jaw plates?
Aftermarket jaw plates from reputable manufacturers offer:
- 20-35% cost savings with OEM-equivalent performance
- Access to advanced grades (TiC inserts) not always available from OEM
- Faster delivery: 3-4 weeks vs. 8-12 weeks OEM
- Custom profile optimization for your application
Ensure aftermarket plates meet dimensional tolerances (±2mm) and include material certifications.
What is your lead time for jaw plates?
- Stock patterns (500+ models): 3-4 weeks including shipping
- Express service: 2 weeks (15% premium)
- Custom/reverse-engineered: 5-8 weeks first order, then stocked
We maintain pattern inventory for popular Metso, Sandvik, Terex, Powerscreen, and Kleemann models.
Do you provide technical support?
Yes, comprehensive support included:
- Remote phone/video installation guidance (free)
- Detailed procedures with torque specifications
- Application engineering for material selection
- On-site commissioning for large projects (quoted separately)
Our engineers have 35+ years combined experience in crusher wear parts.
Get Your Custom Jaw Plate Quote in 24-48 Hours
Connect with our engineering experts for precise material recommendations and competitive pricing. No hassle, no sales pressure – just technical solutions.
Trusted by 500+ global aggregate & mining operations
Prefer a direct consultation?
Email our Engineering Team: info@atfcs.com
Call Our Experts: +1 308 465 1950
Or visit our dedicated contact page
Our Streamlined RFQ Process: What Happens Next?
-
1
Instant Confirmation
You’ll receive a confirmation of your inquiry immediately, ensuring receipt.
-
2
Expert Technical Review
Our dedicated applications engineering team meticulously analyzes your specific requirements and operating conditions.
-
3
Detailed Custom Quotation
Receive a comprehensive pricing proposal and material recommendation within 24-48 business hours.
Serving aggregate, mining, cement & recycling industries globally.
OEM-compatible parts backed by ISO 9001 standards and expert technical support.
Your technical and commercial information is protected and never shared.
“ATF delivered exactly what we needed. Fast response, competitive pricing, and jaw plates that lasted 35% longer than our previous supplier—significantly reducing our cost per ton.”
— Operations Manager, Leading Chilean Mining Company
Essential Jaw Plate Technical Downloads
Access critical resources for optimized jaw plate selection, Mn grade comparison, tooth profile guidance, and proven operational optimization strategies to maximize your crushing uptime and profitability.
-
PDF Jaw Plate Material Selection & Engineering Guide
Comprehensive guide to Mn grades (Mn13/Mn18/Mn22), tooth profiles, TiC insert applications, and setup optimization for maximum wear life and cost-per-ton reduction.
-
PDF Global Jaw Crusher Compatibility List (2025 Edition)
Expanded cross-reference for Metso C-Series, Sandvik CJ/QJ, Terex Finlay J-Series, Powerscreen Premiertrak, Kleemann MC, and 50+ jaw crusher models with part references.
-
PDF Installation, Maintenance & Optimization Manual
Best practices for safe change-out procedures, torque specifications, CSS monitoring, flip schedules, and feed optimization techniques for maximum jaw plate wear life.
-
PDF Quality Control Certificates & Performance Data
Access detailed hardness testing results, chemistry analysis documentation, ISO 9001 quality certificates, and comprehensive material traceability for ATF jaw plates.
Meet Our Leading HSI Wear Parts Engineering Experts
Our team of metallurgical and applications engineers is dedicated to optimizing your crushing performance and reducing your cost per ton. Connect directly with the minds behind ATF’s innovative blow bar solutions.

Bao Xiuru
Product Manager, HSI Wear Parts — 18+ years optimizing HSI blow bar alloys and designs for maximum wear life in aggregate & recycling plants. Specializes in cost-per-ton reduction strategies.

Zhang Lin
Senior Foundry Engineer, Metallurgy Specialist — Over 20 years of hands-on experience in the advanced casting and heat treatment of high-performance wear parts, focusing on metallurgical integrity and alloy innovation.